NT-I7 is a Unique T Cell Amplifier
Interleukin-7 (IL-7) is Central to T Lymphocyte Development and Survival
IL-7 acts through the IL-7 receptor (IL-7R), which is expressed on naïve and memory CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. Thus, IL-7 promotes the proliferation, maintenance, and functionality of these key T cell subsets mediating immune responses. On the other hand, regulatory T cells, a subset involved in limiting immune responses, express low levels of IL-7R and are less reactive to IL-74.
At NeoImmuneTech, we are exploring the utility of NT-I7-related therapeutics in enhancing immune function.
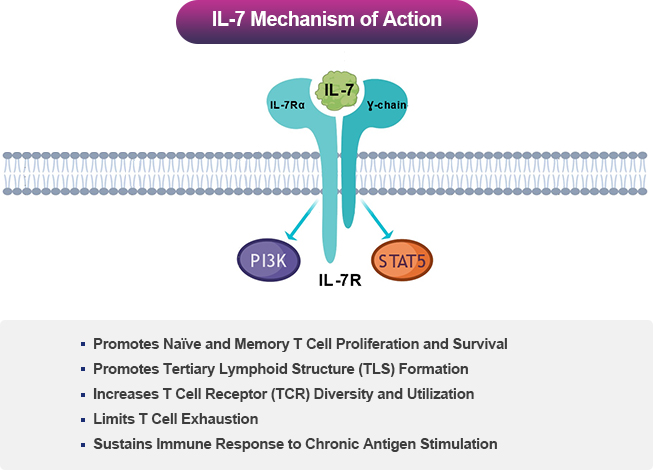
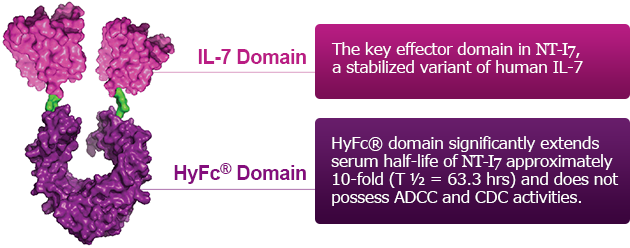
NT-I7 is a More Potent, Stable, and Long-Acting Human IL-7
The HyFc® domain extends the half-life of IL-7, thereby enhancing bioavailability which provides better potency and stability.
NT-I7 Boosts T Cell Numbers and Functionality to Enhance Immune Function and Potentially Provide Greater Therapeutic Benefits to Patients

1. Mazzucchelli, Renata, and Scott K. Durum. "Interleukin-7 receptor expression: intelligent design." Nature Reviews Immunology 7.2 (2007): 144-154.
2. Fry, Terry J., and Crystal L. Mackall. "Interleukin-7: from bench to clinic." Blood, The Journal of the American Society of Hematology 99.11 (2002): 3892-3904.
3. Ponchel, Frederique, et al. "Interleukin-7 deficiency in rheumatoid arthritis: consequences for therapy-induced lymphopenia." Arthritis Res Ther 7.1 (2004): R80.
4. Seddiki, N. Santner-Nanan B, Martinson J, Zaunders J, Sasson S, Landay A, Solomon M, Selby W, Alexander SI, Nanan R, Kelleher A, Fazekas de St Groth B. "Expression of interleukin (IL)-2 and IL-7 receptors discriminates between human regulatory and activated T cells." J Exp Med 203 (2006): 1693-1700.
Homeostatic Proliferation
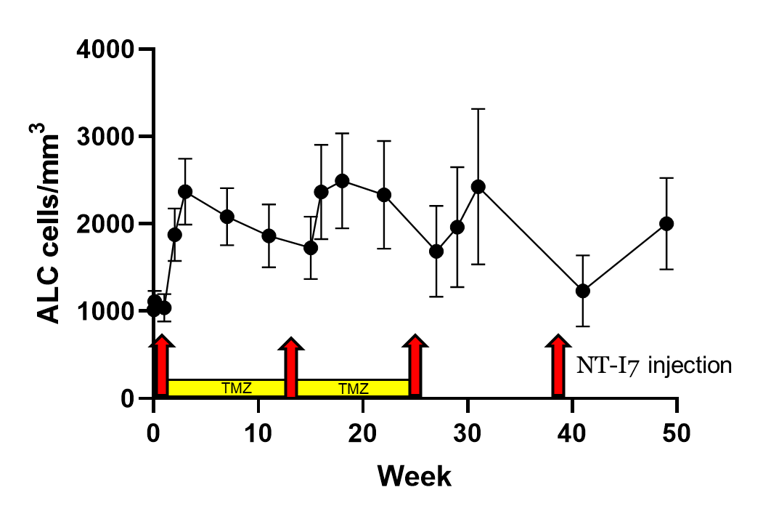
Absolute lymphocyte counts (ALC)
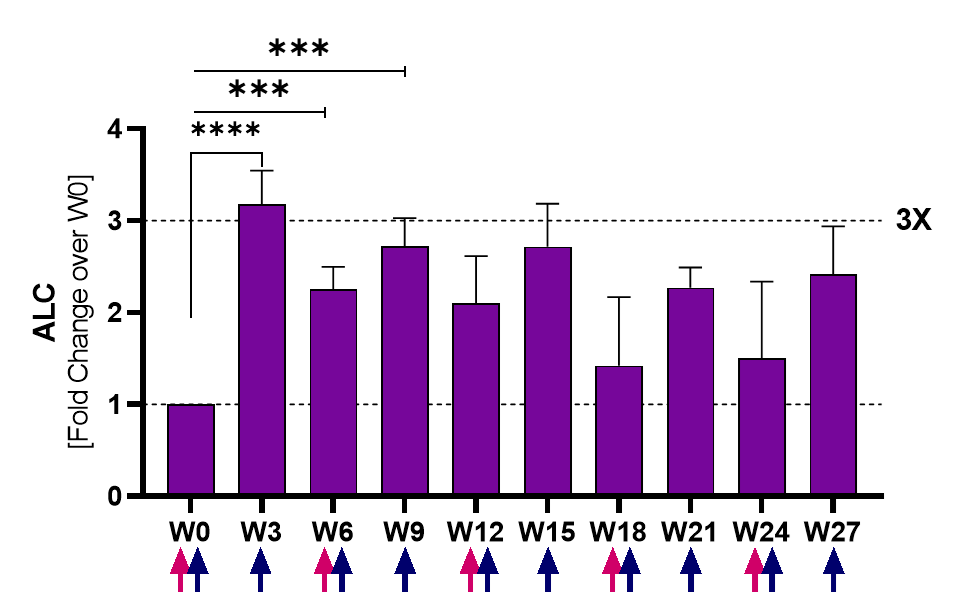
Lymphocytes (ALC) significantly increased (3x over baseline) by week 3 and remained elevated for the duration of the follow-up. Analysis based on 17 evaluable patients.
Lymphocytes (ALC) increased and remain elevated even when patients were receiving chemotherapy (temozolomide, TMZ).
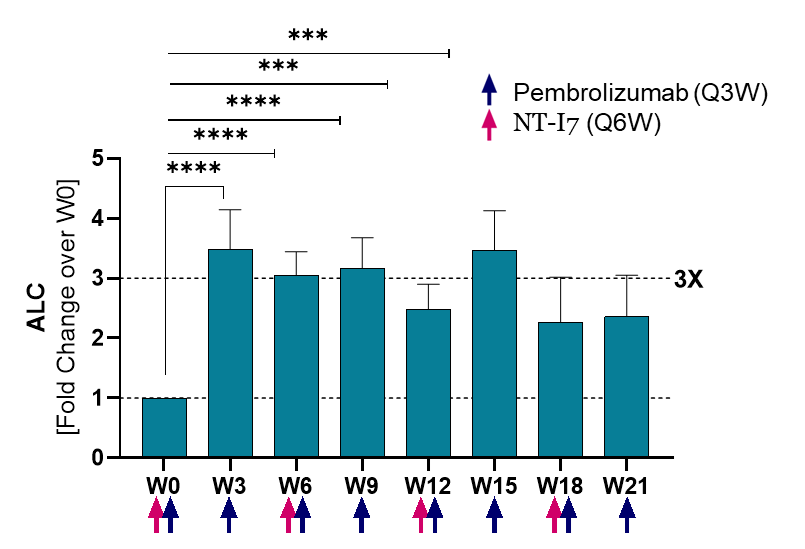
Lymphocytes (ALC) significantly increased (3x over baseline) by week 3 and remained elevated for the duration of the follow-up. Analysis based on 17 evaluable patients.

Lymphocytes (ALC) increased and remain elevated even when patients were receiving chemotherapy (temozolomide, TMZ).
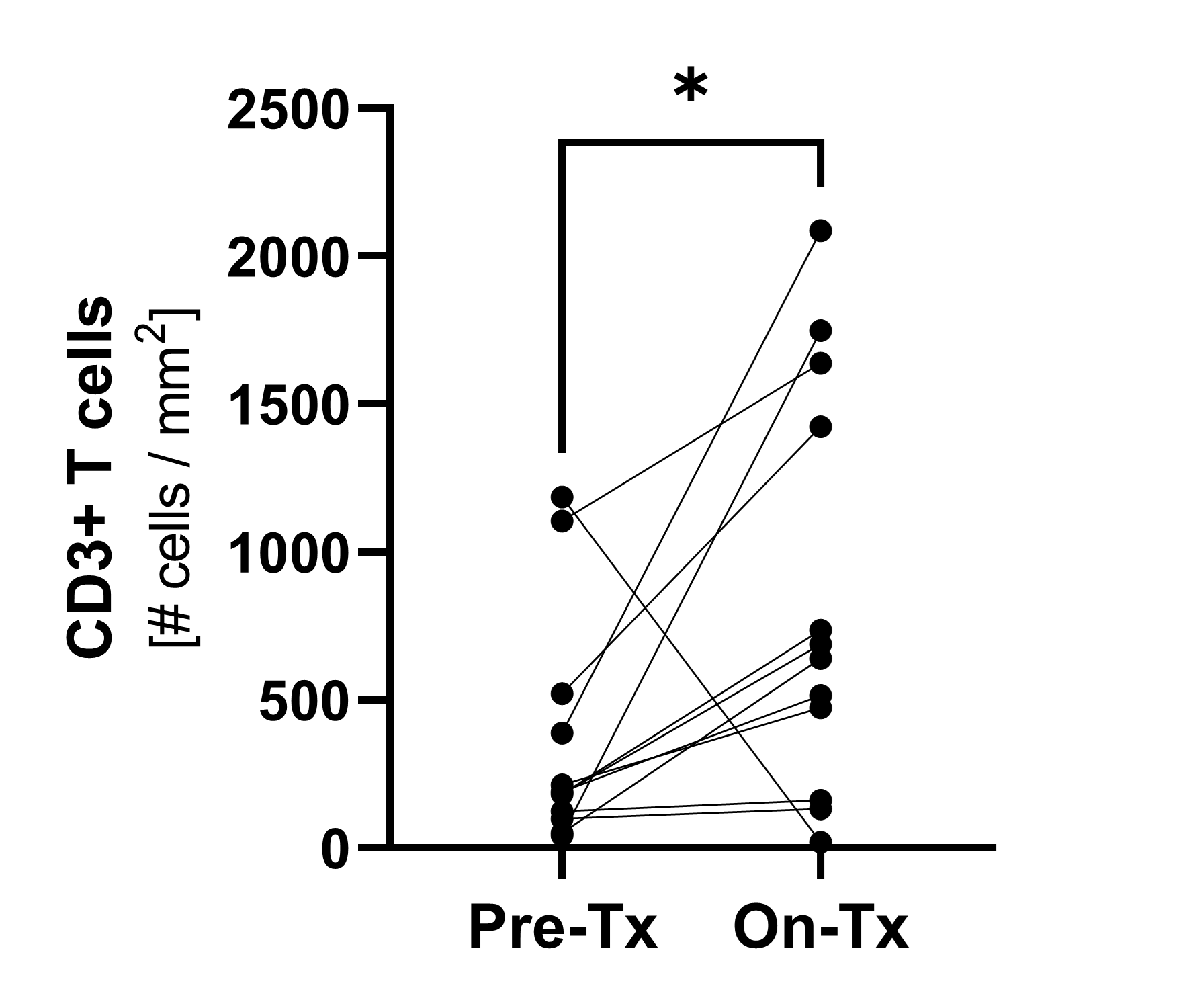
CD4+ and CD8+ T cells
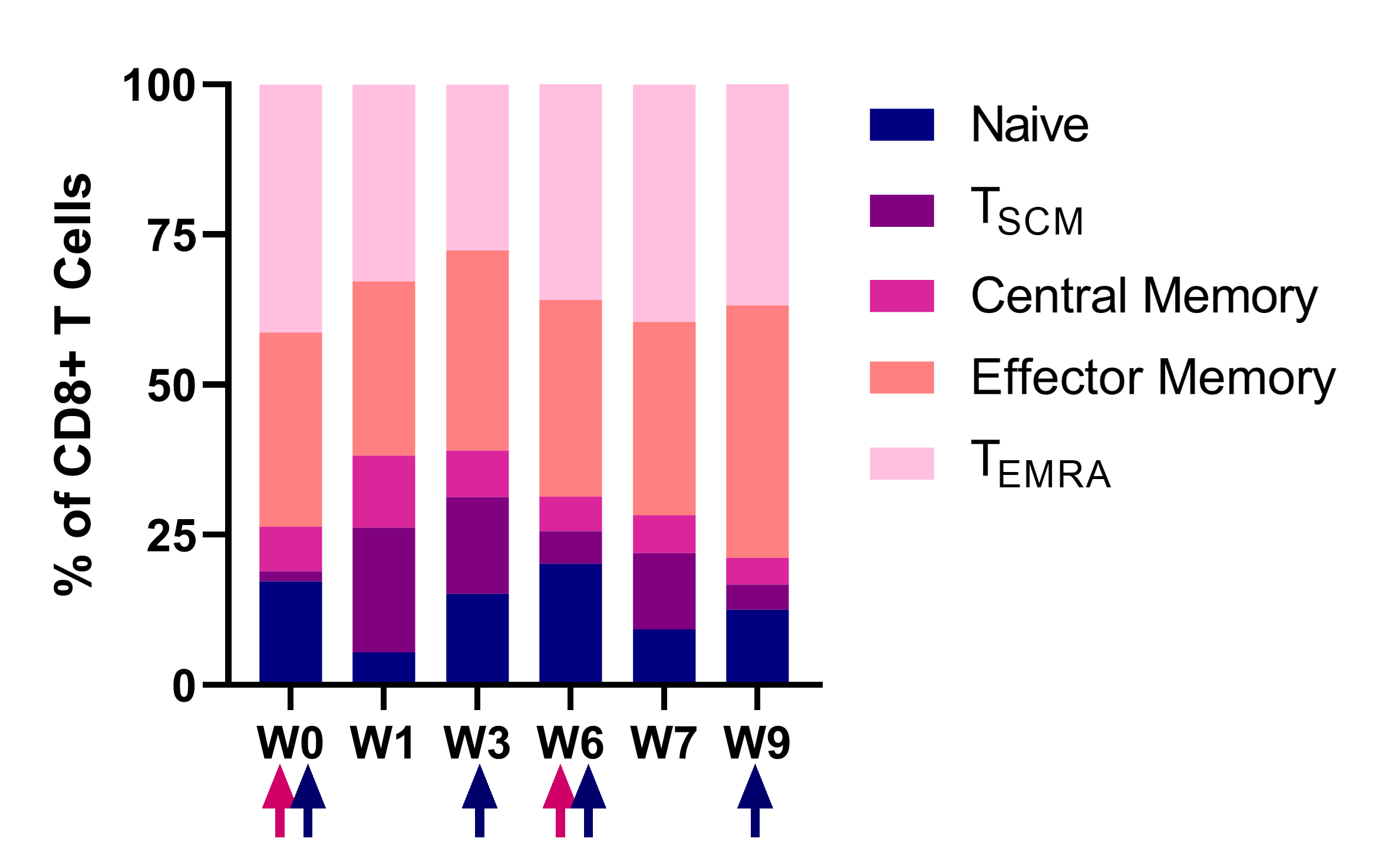
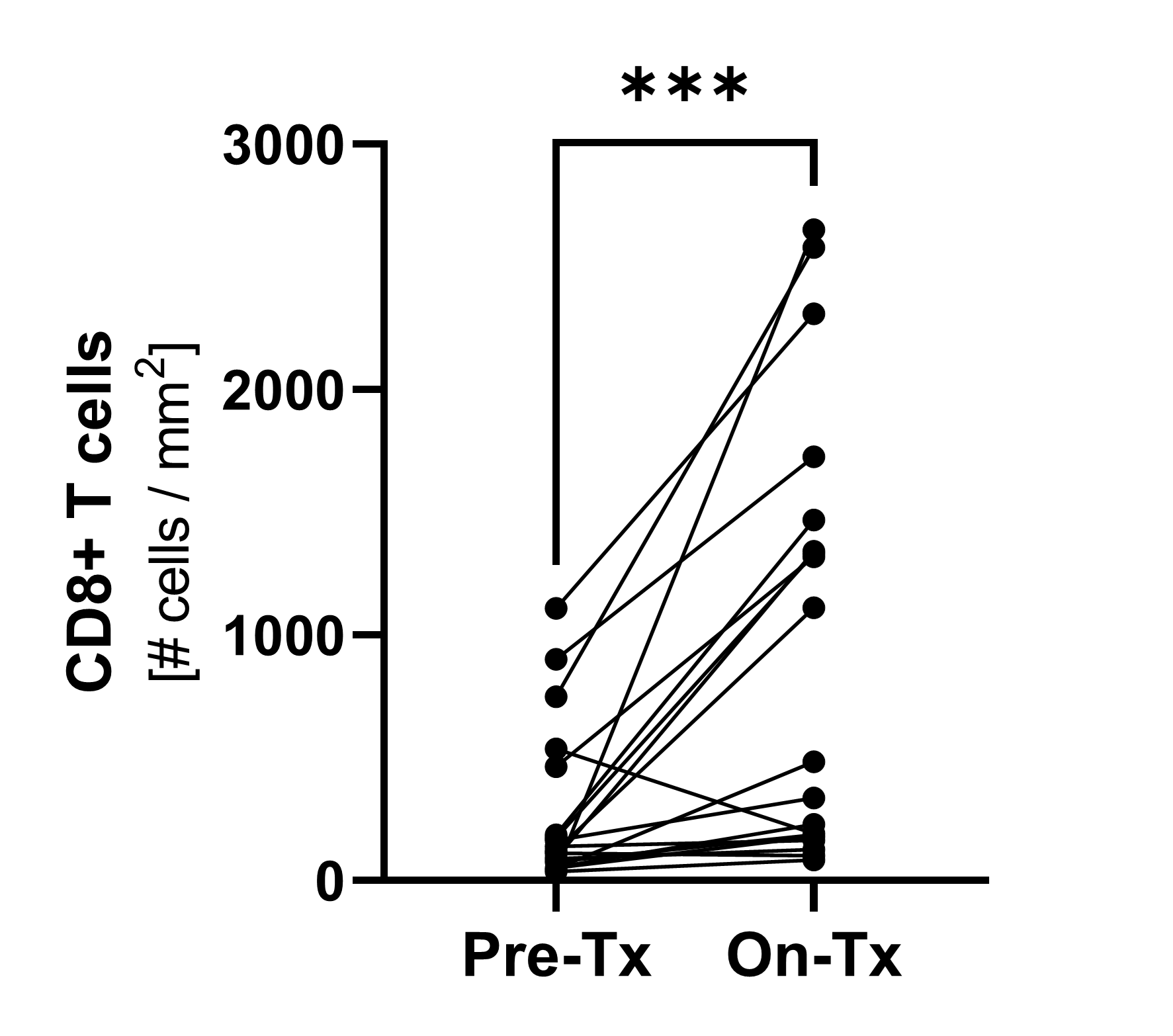
CD8+ T cells subsets
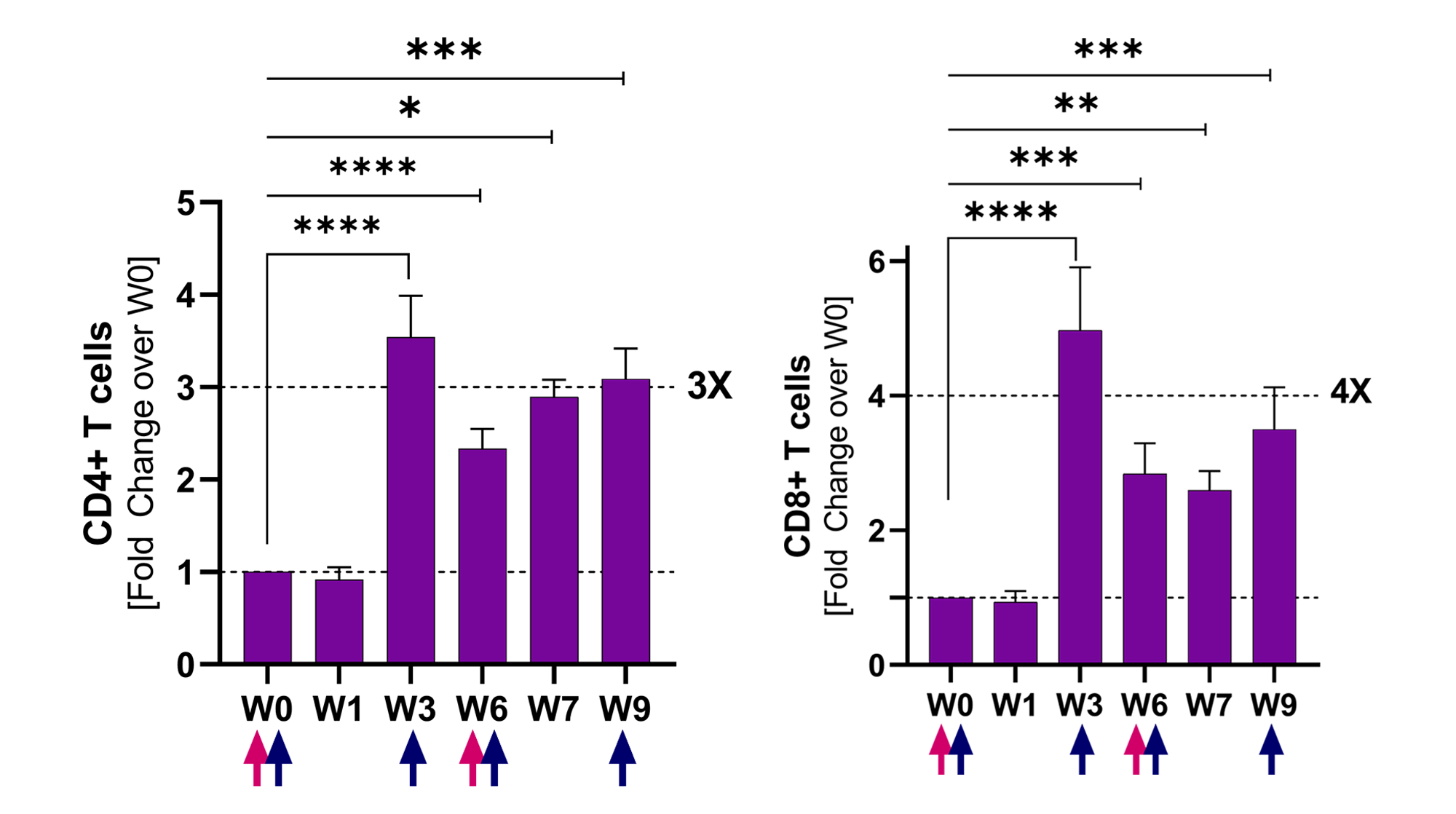
CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, following the same pattern, increased 4x over baseline by week 3 and remained increased until week 9 (last measurement). Analysis based on 17 evaluable patients.
(*p≤0.05; **p≤0.001; ***p≤0.0001; ***p≤0.00001)
Dynamics of the CD8+ T cell subsets after NT-I7 administration. The associated upregulation of Ki67 (data not shown), a marker of cell proliferation, suggests that proliferation, rather than re-distribution, is driving the increase of T cells.
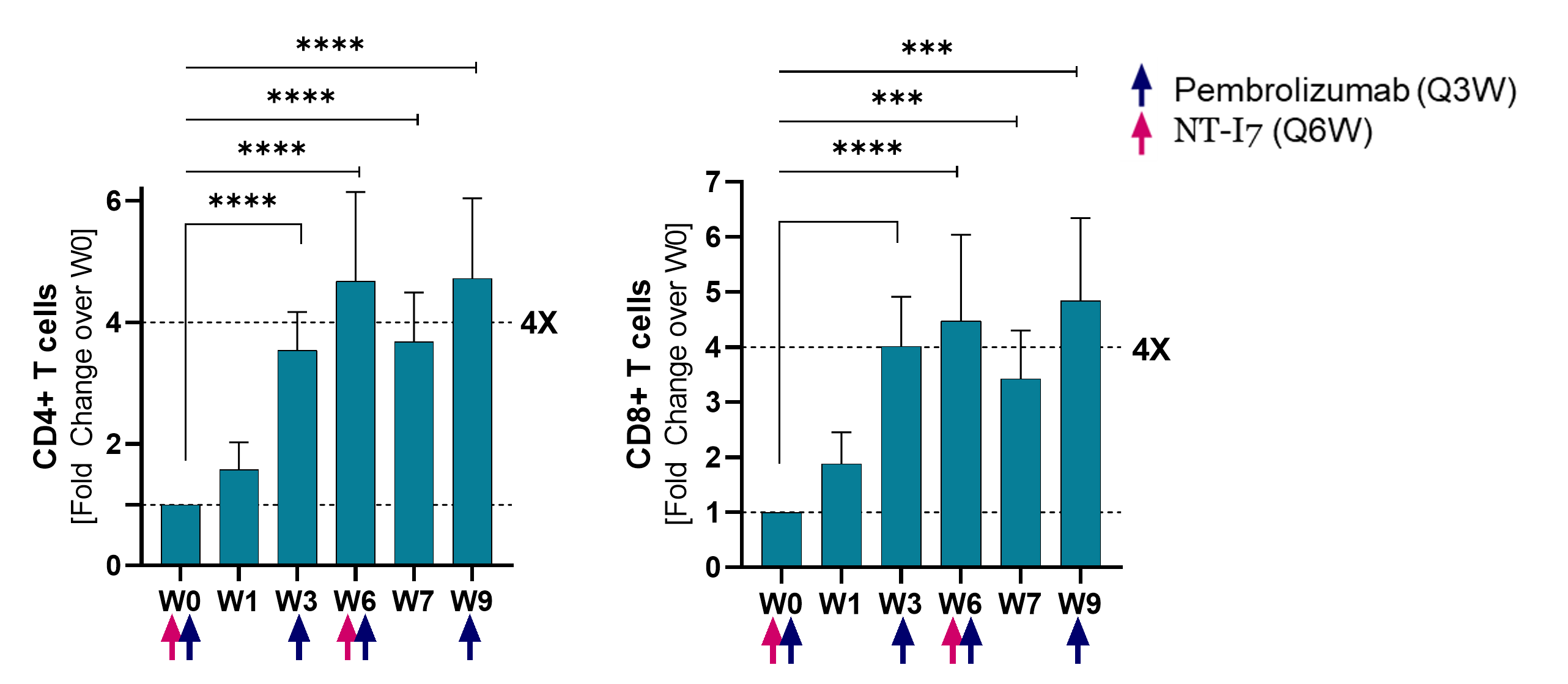
CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, following the same pattern, increased 4x over baseline by week 3 and remained increased until week 9 (last measurement). Analysis based on 17 evaluable patients.
(*p≤0.05; **p≤0.001; ***p≤0.0001; ***p≤0.00001)
CD8+ T cells subsets
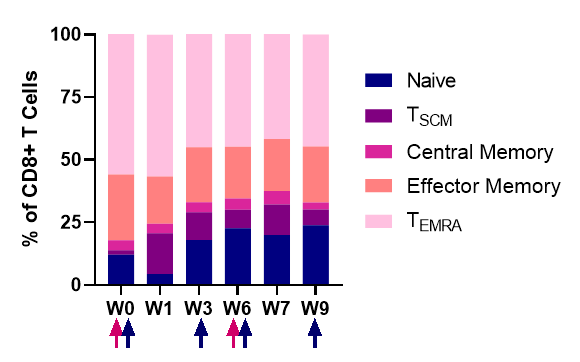
Dynamics of the CD8+ T cell subsets after NT-I7 administration. The associated upregulation of Ki67 (data not shown), a marker of cell proliferation, suggests that proliferation, rather than re-distribution, is driving the increase of T cells.
Source
Naing A, Kim R, Barve M. “Preliminary biomarker and clinical data of a phase 2a study of NT-I7, a long-acting interleukin-7, plus pembrolizumab: cohort of subjects with checkpoint inhibitor-naïve advanced pancreatic cancer” (2021) J Immunoth Cancer 9(Suppl 2):A1-A1054
Zhou A, Rettig M, Foltz Jennifer. “NT-I7,a long-acting interleukin-7, promotes expansion of CD8 T cells and NK cells and immune activation in patients with newly diagnosed high-grade gliomas after chemoradiation” Poster Presented at SITC; Sep. 13th, 2021; Washington, D.C.
Increased Tumor Infiltrating Lymphocytes (TIL)
Plasmatic chemokines
Tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL)
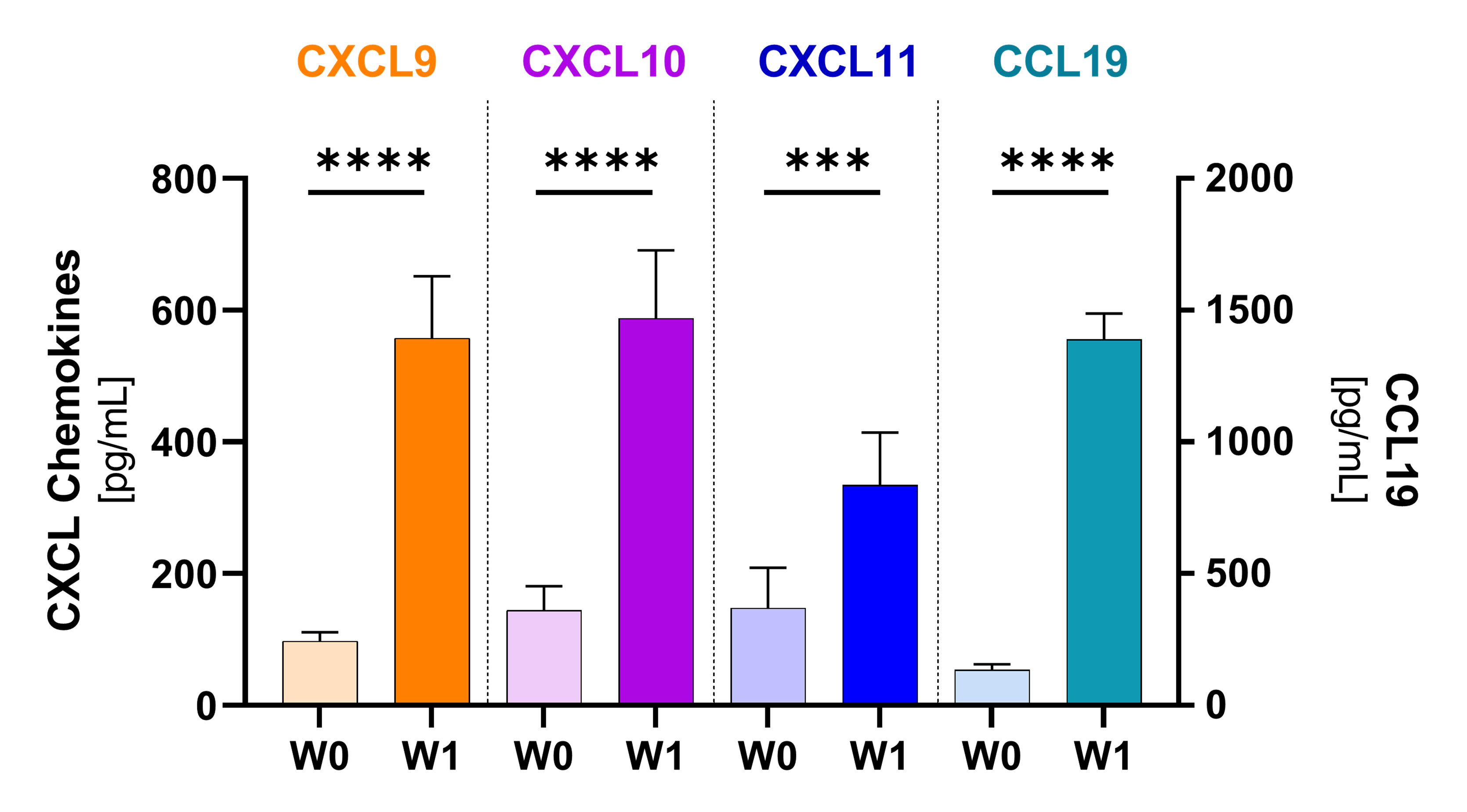
Potent chemoattractants and mediators of TLS formation significantly increased after the first NT-I7+pembro dose. These chemokines recruit lymphocytes into the tumor and facilitate T cell anti-tumor activity. Analysis based on 17 evaluable patients. (*p≤0.05; **p≤0.001; ***p≤0.0001; ***p≤0.00001)
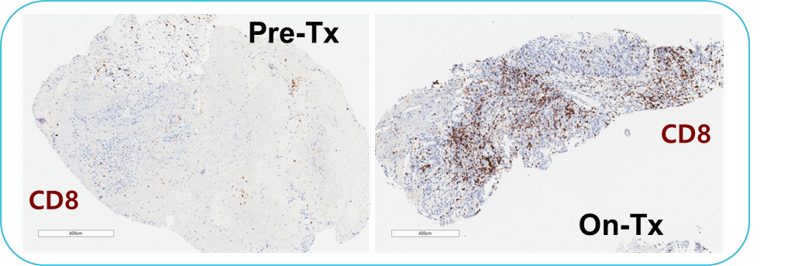
Pre-Tx = Pre-treatment & On-Tx = On-treatment.
Representative pre- and on-treatment paired biopsies for a subject with clear cell ovarian cancer. Immunohistochemical staining showed a significant increase of CD8+ T cells (brown) in the on-treatment sample.
Plasmatic chemokines
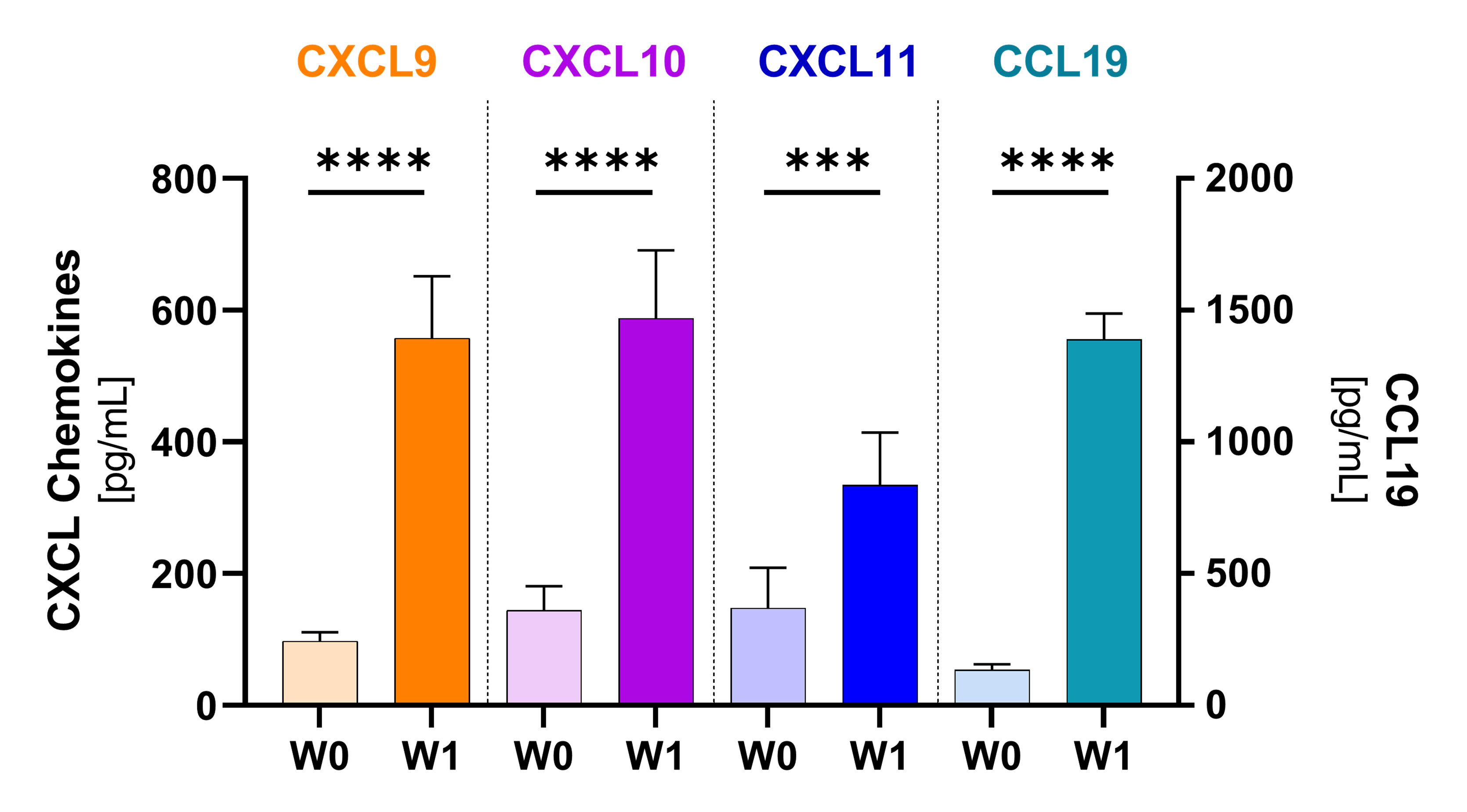
Potent chemoattractants and mediators of TLS formation significantly increased after the first NT-I7+pembro dose. These chemokines recruit lymphocytes into the tumor and facilitate T cell anti-tumor activity. Analysis based on 17 evaluable patients. (*p≤0.05; **p≤0.001; ***p≤0.0001; ***p≤0.00001)
Tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL)

Pre-Tx = Pre-treatment & On-Tx = On-treatment.
Representative pre- and on-treatment paired biopsies for a subject with clear cell ovarian cancer. Immunohistochemical staining showed a significant increase of CD8+ T cells (brown) in the on-treatment sample.
Source
Kim R, Barve M, Mamdani H, “Initial biomarker and clinical data of a phase 2a study of NT-I7, a long-acting interleukin-7, plus pembrolizumab: cohort of subjects with checkpoint inhibitor-naïve advanced MSS-colorectal cancer” Poster Presented at SITC; Sep. 13th, 2021; Washington, D.C.
NeoImmuneTech, Phase 1, FIH study
TILs by Immunofluorescence
TILs and efficacy
TILs by Immunofluorescence


Pooled data of pre-treatment and on-treatment paired biopsies showed a significant increase of CD8+ T cell infiltration. *p<0.05; ***p<0.0001
TILs and efficacy


Pooled data of pre-treatment and on-treatment paired biopsies showed a significant increase of CD8+ T cell infiltration. *p<0.05; ***p<0.0001
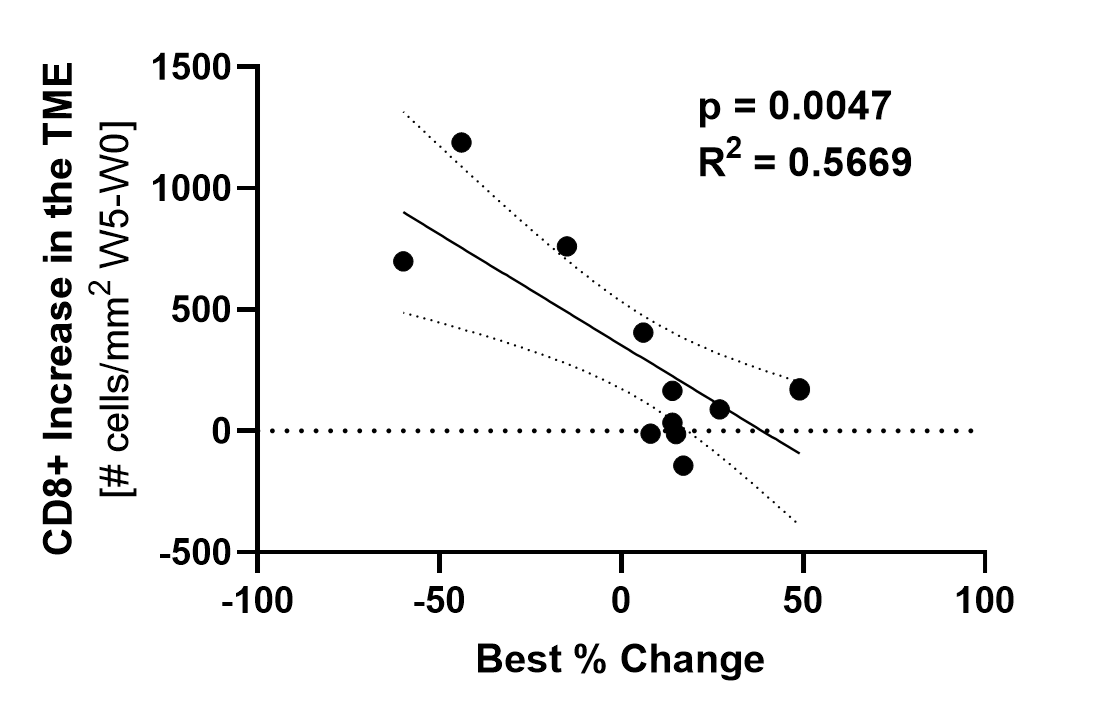
Subjects with a higher increase in TILs (y axis) experienced greater tumor reduction (x axis) with treatment.
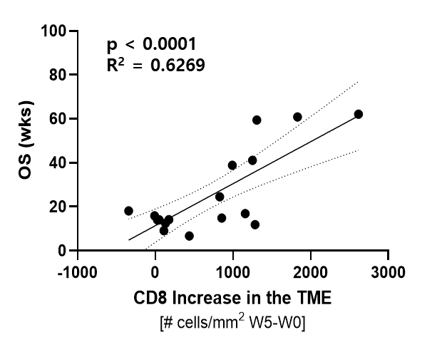
Subjects with a higher increase in TILs (x axis) had higher overall survival (OS) (y axis).
Wks = weeks
Source
Naing A, Ferrando-Martinez S, Wolfarth A, "NT-I7 plus pembrolizumab combination treatment enhances infiltration of PD-1+ T cells and provides a more immunogenic tumor microenvironment: Biomarker data from the NIT-110 study" Poster Presented at ESMO; Sep. 1st, 2022; Paris, France.
Naing A, Ferrando-Martinez S, Ware M, "NT-I7, a long-acting IL-7, plus pembrolizumab favors CD8 T-cell infiltration in liver metastases of heavily pre-treated, immunologically cold, MSS-colorectal and pancreatic cancer" Oral Presentation Presented at SITC; Nov 11, 2022; Boston, MA.
Increased T-Cell Receptor (TCR) Clonality in TIL
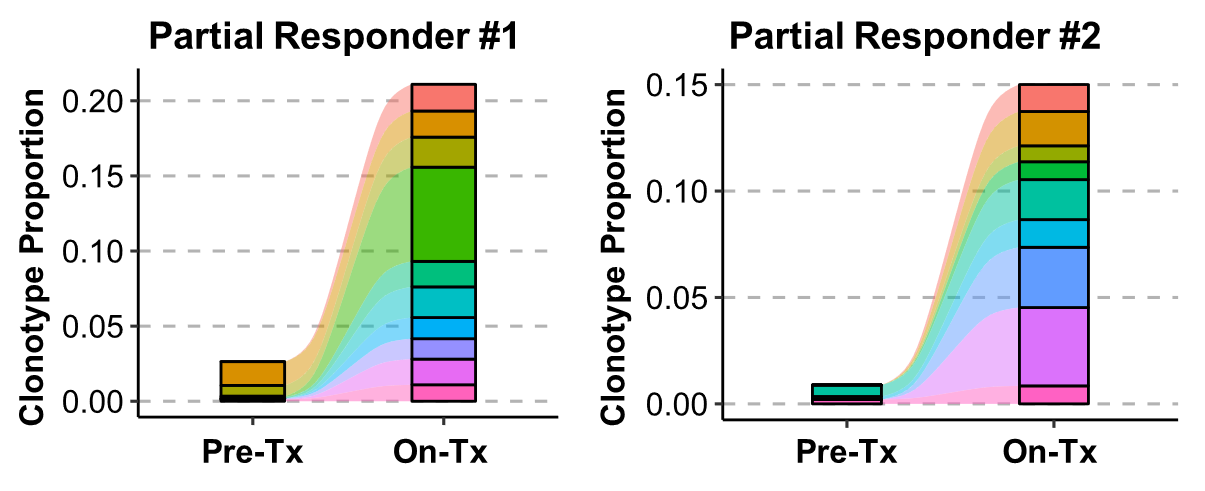
Source
Naing A, Ferrando-Martinez S, Wolfarth A, "NT-I7 plus pembrolizumab combination treatment enhances infiltration of PD-1+ T cells and provides a more immunogenic tumor microenvironment: Biomarker data from the NIT-110 study" Poster Presented at ESMO; Sep. 1st, 2022; Paris, France.
Induction of Stemness
Stem-cell memory CD8+ T cells (Tscm)
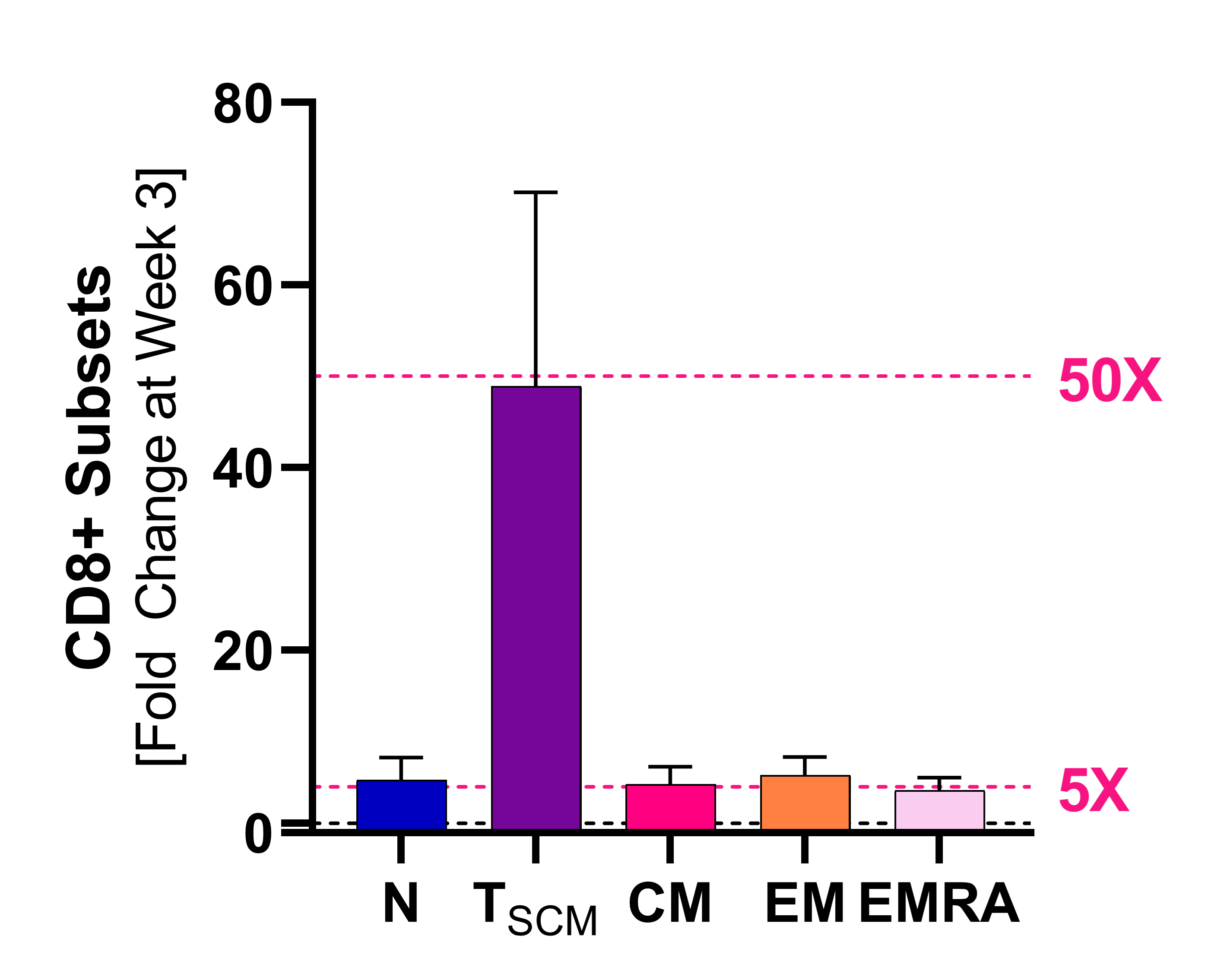
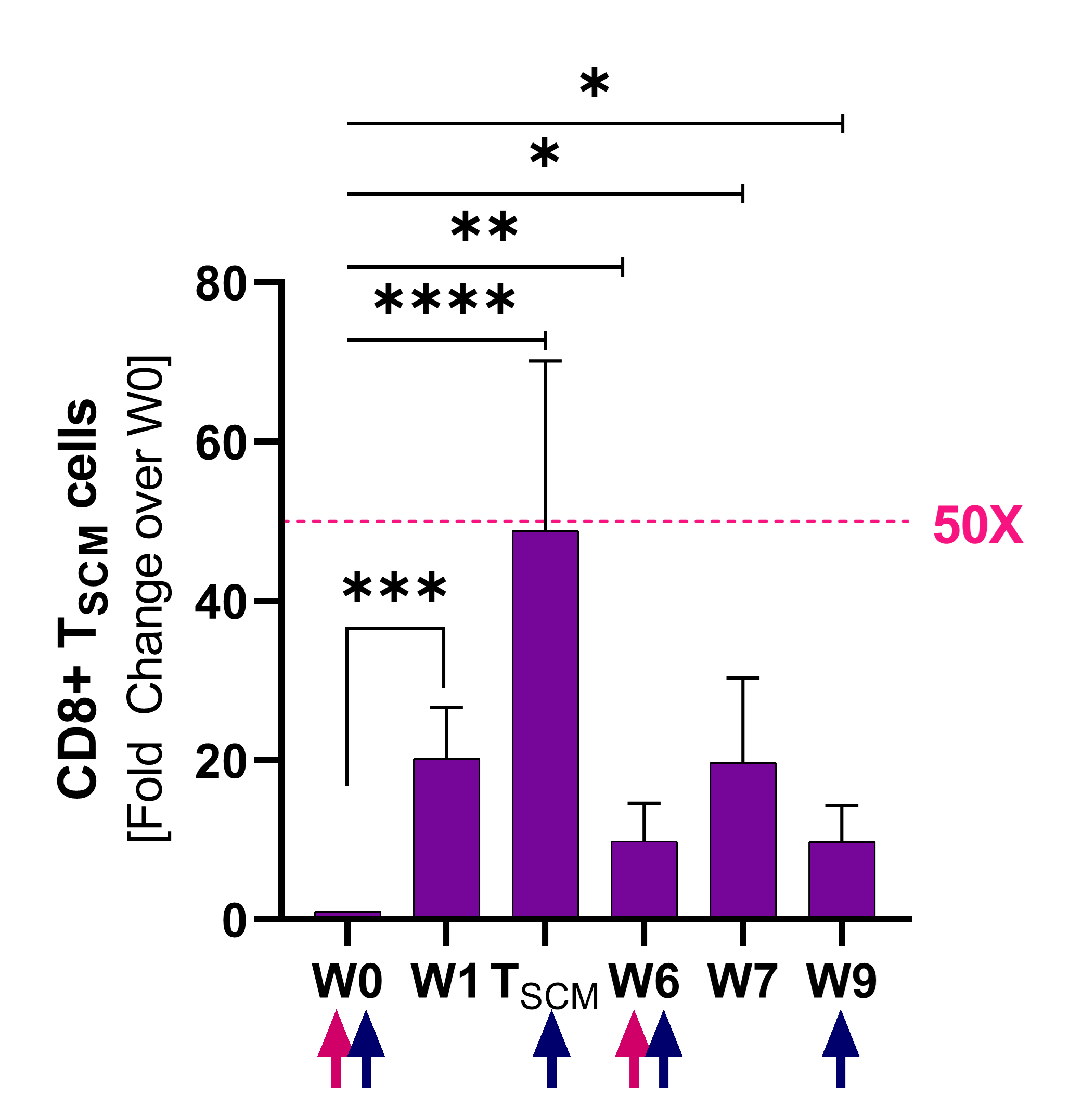
Source
Naing A, Kim R, Barve M. “Preliminary biomarker and clinical data of a phase 2a study of NT-I7, a long-acting interleukin-7, plus pembrolizumab: cohort of subjects with checkpoint inhibitor-naïve advanced pancreatic cancer” Poster Presented at SITC; Sep. 13th, 2021; Washington, D.C.
Scientific Publications
NT-I7 Posters and Presentations – Clinical studies and translational research
- Naing A, Mamdani H, Barve M, "NT-I7 (efineptakin alfa), a long-acting IL-7, in combination with pembrolizumab improves T cell fitness in heavily pretreated subjects with gastrointestinal tumors." Poster Presented At SITC; November 1-5, 2023; San Diego, CA (Click Here )
- Lisco A, Ye P, Anderson M, "Cytokine-based immunotherapy with long-acting human recombinant IL-7 in HPV-related diseases associated with idiopathic CD4 lymphopenia." Poster Presented At ICIS; October 15-18, 2023; Athens, Greece
- Perez-Diez A, Liu X, Bennett A, "A long-acting form of recombinant human IL-7 shows biologic effect in both a pre-clinical model and a clinical pilot study of Idiopathic CD4 Lymphopenia." Poster Presented At ICIS; October 15-18, 2023; Athens, Greece
- Webb M, Burns T, Twohy E, "Efficacy and Safety Study of Neoadjuvant Efineptakin alfa (NT-I7) and Pembrolizumab in Recurrent Glioblastoma." Poster Presented At ASCO; June 2-6, 2023; Chicago, IL (Click Here )
- Ghobadi A, Budde L., Galal A, "A Phase 1b Dose Expansion Study Evaluating Safety, Preliminary Anti-Tumor Activity, and Accelerated T Cell Reconstitution with NT-I7 (Efineptakin Alfa), a Long-Acting Human IL-7, Administered Following Tisagenlecleucel in Subjects with Relapsed/Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma." Poster Presented At ASH; Dec 10-13, 2022; New Orleans, LA (Click Here )
- Naing A, Ferrando-Martinez S, Ware M, "NT-I7, a long-acting IL-7, plus pembrolizumab favors CD8 T-cell infiltration in liver metastases of heavily pre-treated, immunologically cold, MSS-colorectal and pancreatic cancer" Oral Presentation Presented at SITC; Nov 11, 2022; Boston, MA. (Click Here )
- Butt O, Tao Y, Huang J, "A phase I/II study evaluating the safety and efficacy of a novel long-acting interleukin-7, NT-I7, for patients with newly diagnosed high-grade gliomas after chemoradiotherapy" Poster Presented at SITC; Nov 11, 2022; Boston, MA. (Click Here )
- Kang H, Spitzer M, Kim MO, "NT-I7 for the treatment of locally recurrent squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck undergoing salvage surgery: a clinical trial in progress" Poster Presented at SITC; Nov 10, 2022; Boston, MA (Click Here )
- Naing A, Ferrando-Martinez S, Wolfarth A, "NT-I7 plus pembrolizumab combination treatment enhances infiltration of PD-1+ T cells and provides a more immunogenic tumor microenvironment: Biomarker data from the NIT-110 study" Poster Presented at ESMO; Sep. 1st, 2022; Paris, France. (Click Here )
- Kim R, Mamdani H, Brave M, "Phase 2a Study of NT-I7, a Long-Acting Interleukin-7, plus Pembrolizumab: Cohort of Subjects with Checkpoint Inhibitor-Naïve Advanced MSS-Colorectal Cancer" Poster Presented at ESMO-GI; Jul. 1st, 2022; Barcelona, Spain. (Click Here )
- Naing A, Mamdani H, Brave M, "Phase 2a Study of NT-I7, a Long-Acting Interleukin-7, plus Pembrolizumab: Cohort of Subjects with Checkpoint Inhibitor-Naïve Advanced Pancreatic Cancer" Poster Presented at ESMO-GI; Jun. 30th, 2022; Barcelona, Spain. (Click Here )
- Gastman B, Fling S, Ansstas G, "A phase 1b/2a study of safety and efficacy of NT-I7 in combination with anti-PD-L1 (atezolizumab) in patients with anti-PD-1/PD-L1 naïve or relapsed/refractory (R/R) high-risk skin cancers: The phase 1b report." Poster Presented at ASCO; Jun. 6th, 2022; Chicago, IL. (Click Here )
- Naing A, Mamdani H, Brave M, "Efficacy and safety of NT-I7, long-acting interleukin-7, plus pembrolizumab in patients with advanced solid tumors: Results from the phase 2a study." Poster Presented at ASCO; Jun. 5th, 2022; Chicago, IL. (Click Here ) **Selected for poster discussion session
- Ghobadi A, Budde L, Galal A, "Trial in progress: A phase 1b study evaluating the safety, tolerability, and preliminary anti-tumor activity of NT-I7 (efineptakin alfa), a long-acting human IL-7, post-tisagenlecleucel in subjects with relapsed/refractory large B-cell lymphoma" Poster Presented at ASCO; Jun. 4th, 2022; Chicago, IL. (Click Here )
- Sohn J, Kim G, Lee K, “Phase 1b/2 study of GX-I7 plus pembrolizumab in patients with refractory or recurrent (R/R) metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (mTNBC): The KEYNOTE-899 Study.” Poster Presented at ASCO; Jun. 1st, 2022; Chicago, IL.* (Click Here )
- Campian Jian Li, et al. “A phase I/II study evaluating the safety and efficacy of a novel long-acting interleukin-7, NT-I7, for patients with newly diagnosed high-grade gliomas after chemoradiotherapy” Oral Presentation Presented at SNO; Nov 19th, 2021; Boston, MA. (Click Here )
- Zhou A, Rettig M, Foltz Jennifer. “NT-I7,a long-acting interleukin-7, promotes expansion of CD8 T cells and NK cells and immune activation in patients with newly diagnosed high-grade gliomas after chemoradiation” Poster Presented at SITC; Sep. 13th, 2021; Washington, D.C. (Click Here )
- Naing A, Kim R, Barve M. “Preliminary biomarker and clinical data of a phase 2a study of NT-I7, a long-acting interleukin-7, plus pembrolizumab: cohort of subjects with checkpoint inhibitor-naïve advanced pancreatic cancer” Poster Presented at SITC; Sep. 13th, 2021; Washington, D.C. (Click Here )
- Kim R, Barve M, Mamdani H, “Initial biomarker and clinical data of a phase 2a study of NT-I7, a long-acting interleukin-7, plus pembrolizumab: cohort of subjects with checkpoint inhibitor-naïve advanced MSS-colorectal cancer” Poster Presented at SITC; Sep. 13th, 2021; Washington, D.C. (Click Here )
- Campian Jian Li, et al. “A phase I/II study to evaluate the safety and efficacy of a novel long-acting interleukin-7, NT-I7, for patients with newly diagnosed high-grade gliomas after chemoradiotherapy: The interim result of the phase I data.” Poster Presented at ASCO; May. 28th, 2021; Virtual Presentation. (Click Here )
- Naing A, Fan J, Lee B, “Safety, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics profiles and preliminary antitumor activity of phase 1b/2a study of NT-I7, a long-acting interleukin-7, plus pembrolizumab in patients with advanced solid tumors: The phase 1b data report.” Poster Presented at ASCO; May. 28th, 2021; Virtual Presentation. (Click Here )
- Sohn J, Im Y, “Efficacy and safety of GX-I7 plus pembrolizumab for heavily pretreated patients with metastatic triple negative breast cancer: The Phase 1b/2 KEYNOTE-899 Study.” Poster Presented at SITC; Oct. 10th, 2020; Virtual Presentation.* (Click Here )
- Sohn J, Park K, Ahn H, “Preliminary safety and efficacy of GX-I7, a long-acting interleukin-7, in combination with pembrolizumab in patients with refractory or recurrent metastatic triple negative breast cancer (mTNBC): Dose escalation period of Phase Ib/II study (KEYNOTE-899).” Poster Presented at ASCO; May. 25th, 2020; Virtual Presentation.* (Click Here )
- Lee S, Choi D, Heo M, “Hyleukin-7, a long-acting interleukin-7, increased absolute lymphocyte counts after subcutaneous and intramuscular administration in healthy subjects.” Poster Presented at AACR; Mar. 30th, 2019; Atlanta, GA.* (Click Here )
- Heo M, Sohn J, Lee M, “Phase 1b study of GX-I7, a long-acting interleukin-7, evaluating the safety, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics profiles in patients with advanced solid cancers.” Poster Presented at SITC; Nov. 6th, 2019; National Harbor, MD.* (Click Here )
NT-I7 Posters and Presentations – Nonclinical research
- Lee SM, Kim M, Ferrando-Martinez S, "rhIL-7-hyFc (efineptakin-alfa, NT-I7) increases tumor-specific CD8+ T cells despite FOLFOX cytotoxicity effect." Poster Presented At AACR; April 5-10, 2024; San Diego, CA (Click Here )
- Xiang J, Devenport J, Carter A, "An “off-the-shelf” CD2 Universal CAR-T therapy combined with a long-acting IL-7 for T-cell malignancies ." Oral Presented At ASH; December 9-12, 2023; San Diego, CA (Click Here )
- Lee M, Ferrando-Martinez S, Im SK, "NT-I7 and hIL-2/TCB2c combination promotes an immune-stimulatory tumor microenvironment that favors anti-tumor efficacy in combination with checkpoint inhibitors." Poster Presented At SITC; November 1-5, 2023; San Diego, CA (Click Here )
- Li Y, Hu T, Kesarwani A, "Long-acting recombinant interleukin-7, rhIL-7-hyFc, improves survival following oncolytic Zika virus treatment in the SB28 immunosuppressive and treatment-resistant murine glioma model." Poster Presented At SNO; November 16-19, 2023; Vancouver, Canada (Click Here )
- Niavi C, Lee J, Valanparambil R, "Effect of NT-I7 treatment on CD4 T cells during chronic LCMV ." Poster Presented At ICIS; October 15-18, 2023; Athens, Greece
- Lee J, Niavi C, Ahn E, "NT-I7, a long-acting interleukin-7, promotes expansion and mobilization of virus-specific PD-1+Tcf-1+ stem-like CD8 T cells during chronic viral infection." Poster Presented At ICIS; October 15-18, 2023; Athens, Greece
- Lee M, Im SK, Baek S, "The combination of NT-I7 and hIL-2/TCB2c promotes the development of an immune-stimulatory tumor microenvironment that enhances the anti-tumor efficacy in combination with checkpoint inhibitors ." Poster Presented At KAI; September 13-16, 2023; Incheon, Korea
- Chen M, Chen I, Supabphol S, "NT-I7 as an adjuvant to DNA neoantigen vaccination enhances and prolongs neoantigen-specific anti-tumor immunity." Poster Presented At AACR; April 14-19, 2023; Orlando, FL (Click Here )
- Phoon Y, Kai K, Wolfarth A, "NT-I7, a novel long-acting interleukin-7, improves engraftment of patient immune cells and efficacy of anti-PD-1 therapy in a preclinical humanized melanoma model" Poster Presented at SITC; Nov 10, 2022; Boston, MA. (Click Here )
- Lee KJ, Tae N, Kang YW, "Redirecting IL-7-induced bystander tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes by bispecific T cell engager augments antitumor response" Poster Presented at SITC; Nov 10, 2022; Boston, MA. (Click Here )
- Zou Y, Jiao Y, Wolfarth A, "NT-I7, a long-acting recombinant human interleukin-7, enhances T cell reconstitution following total body irradiation" Poster Presented at RRS; Oct 17, 2022; Waikoloa Village, HI. (Click Here )
- Zou Y, Jiao Y, Wolfarth A, "NT-I7, a long-acting recombinant human interleukin-7, enhances T cell reconstitution following total body irradiation" Oral Presentation Presented at RITN; Aug 4, 2022; Alexandria, VA. (Click Here )
- Baek S, Im SK, Lee M, "rhIL-7-hyFc (efineptakin alpha; NT-I7) enhances the anti-tumor response when combined with anti-TIGIT or anti-VEGF" Poster Presented at AACR; Apr. 13th, 2022; New Orleans, LA. (Click Here )
- Baek S, Im SK, Lee M, "rhIL-7-hyFc (efineptakin alpha; NT-I7) enhances the anti-tumor response when combined with hIL-2/TCB2c complex" Poster Presented at AACR; Apr. 13th, 2022; New Orleans, LA. (Click Here )
- Bardahl J, Jiao Y, Wolfarth A, “Effects of a novel long-acting IL-7 on T cell reconstitution following allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation” Poster Presented at Duke Pediatrics Research Retreat; Apr. 28th, 2022; Durham, NC. (Click Here )
- Niavi C, Lee J, McManus D, “Effect of NT-I7 treatment on CD8 T cell differentiation during chronic LCMV” Poster Presented at SIS 2022; Jun. 11th, 2022; Durham, NC. (Click Here )
- Liang T, Li, D, Ferrando-Martinez S, “Influence of NT-I7, an engineered long-acting interleukin-7, on CAR T cell therapy in liver cancer” Poster Presented at PEGS 2022; May 4th, 2022, Boston, MA. (Click Here )
- Campian, Jian Li, et al. ”A novel long-acting interleukin-7 agonist, NT-I7, increases cytotoxic CD8 cells and enhances survival in mouse glioma models.” Oral Presentation Presented at SNO 2020; Virtual Presentation. (Click Here )
- Park S, Kim J, Kang Y, “Combination of rhIL-7-hyFc and anti-PD-L1xCD3ε bispecific antibody enhances antitumor response in mice” Poster Presented at SITC; Nov. 09th 2020; Virtual Presentation. (Click Here )
- Ghosh S, Yan R, Thotala S, “A novel long-acting interleukin-7 agonist, NT-I7, increases cytotoxic CD8+ T cells and enhances survival in mouse glioma models” Poster Presented at SITC; Dec. 10th 2020; Virtual Presentation. (Click Here )
- O'Neal, Julie, et al. "In vivo efficacy of BCMA-iNKT-CAR is enhanced by NT-I7, a long-acting IL-7.” Oral Presentation Presented at 17th International Myeloma Workshop; Sep. 13th, 2019; Boston, MA. (Click Here )
- Campian, Jian Li, et al. "Effect of a novel long-acting interleukin-7 agonist, NT-I7, on survival in mouse models of glioma.” Abstract submitted for ASCO; May. 31st, 2019: e13516. (Click Here )
- Kim J, Hong S, Kim Y, "Hyleukin-7, the Fc-fused interleukin-7, generates anti-tumor activity by modulating both adaptive and innate immune cells in the tumor microenvironment.” Poster Presented at AACR; Mar. 30th, 2019; Atlanta, GA. * (Click Here )
- Cooper ML, Staser KW, Niswonge J, "A Long-Acting Pharmacological Grade Interleukin-7 Molecule Logarithmically Accelerates CART Proliferation, Differentiation, and Tumor Killing.” Poster Presented at TCT-Transplant & Cellular Therapy: Feb. 20th, 2019; Houston, TX. (Click Here )
- Staser KW, Cooper ML, Choi J, "Modeling Sezary Syndrome For Immunophenotyping and Anti-Tumor Effect of Ucart and Long-Acting Interleukin-7 Combination Therapy.” Poster Presented at TCT-Transplant & Cellule Therapy: Feb. 20th, 2019; Houston, TX. (Click Here )
- Staser KW, Cooper ML, Choi J, "Modeling Sezary Syndrome For Immunophenotyping and Anti-Tumor Effect of Ucart and Long-Acting Interleukin-7 Combination Therapy.” Poster Presented at ASH Annual Meeting; Dec. 2nd, 2018; San Diego, CA. (Click Here )
- Cooper M, Staser K, Davenport J, "A long-acting pharmacological grade interleukin-7 molecule logarithmically accelerates UCAR-T proliferation, differentiation, and tumor killing.” Oral Presentation Presented at ASH Annual Meeting; Dec. 2nd, 2018; San Diego, CA. (Click Here )
- Kim J, Choi D, Ji M, "Preclinical evaluation of the anti-tumor activity of Fc-fused interleukin-7 in both monotherapy and combination therapy.” Poster Presented at AACR; Apr. 14th, 2018; Chicago, IL. (Click Here )
Scientific Publications
- Kim, Anhye, et al. "Understanding the pharmacokinetic journey of fc-fusion protein, rhIL-7-hyFc, using complementary approach of two analytical methods, accelerator mass spectrometry and ELISA." Antibody Therapeutics (2024). https://doi.org/10.1093/abt/tbae004
- Kwon, Dong-Il, et al. "Fc-fused IL-7 provides broad antiviral effects against respiratory virus infections through IL-17A-producing pulmonary innate-like T cells." Cell Report Medicine (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xcrm.2023.101362
- Lee, Minji, et al. "rhIL-7-hyFc and hIL-2/TCB2c combination promotes an immune-stimulatory tumor microenvironment that improves anti-tumor efficacy of checkpoint inhibitors." Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer (2024). https://doi.org/10.1136/jitc-2023-008001
- Xiang, Jingyu, et al. "An “off-the-shelf” CD2 Universal CAR-T therapy for T-cell malignancies." Leukemia (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41375-023-02039-z
- O'Neal, Julie, et al. "Anti-myeloma efficacy of CAR-iNKT is enhanced with a long-acting IL-7, rhIL-7hyFc." Blood Advances (2023). https://doi.org/10.1182/bloodadvances.2023010032
- Ware, Michael B. et al. "The Role of Interleukin-7 in the Formation of Tertiary Lymphoid Structures and Their Prognostic Value in Gastrointestinal Cancers" Journal of Immunotherapy and Precision modalPageOne 5.4 (2022): 105-117. https://doi.org/10.36401/JIPO-22-10
- Kim, Sojeong et al. "A single administration of hIL-7-hyFc induces long-lasting T-cell expansion with maintained functions and TCR diversity" Blood Advances (2022). https://doi.org/10.1182/bloodadvances.2021006591
- Kim, Miriam Y. et al. "A long-acting interleukin-7, rhIL-7-hyFc, enhances CAR T cell expansion, persistence, and anti-tumor activity" Nature Communications (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-30860-0
- Wolfarth, Alexandra A. et al. “Advancements of Common Gamma-Chain Family Cytokines in Cancer Immunotherapy” Immune Network (2022). https://doi.org/10.4110/in.2022.22.e5
- Campian, Jian L. et al. “Long-acting recombinant human interleukin-7, NT-I7, increases cytotoxic CD8 + T cells and enhances survival in mouse glioma models” Clinical Cancer Research (2022). https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-0947
- Kim, Miriam Y, et al. “CD7-deleted hematopoietic stem cells can restore immunity after CAR T cell therapy” JCI Insight (2021). https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.149819
- Kim, Ji-Hae, et al. “Cancer immunotherapy with T-cell targeting cytokines: IL-2 and IL-7.” BMB Reports (2021). https://doi.org/10.5483/BMBRep.2021.54.1.257
- Foluso O Ademuyiwa, et al. “Immunogenomic profiling and pathological response results from a clinical trial of docetaxel and carboplatin in triple-negative breast cancer.” Breast Cancer Research and Treatment (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-021-06307-3
- Kim, Sora, et al. “Fc-fused IL-7 mobilizes long-term HSCs in a pro-B cell-dependent manner and synergizes with G-CSF and AMD3100.” Leukemia(2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41375-021-01274-6
- Kim, Ji-Hae, et al. “Hybrid Fc-fused interleukin-7 induces an inflamed tumor microenvironment and improves the efficacy of cancer immunotherapy.” Clinical and Translational Immunology (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/cti2.1168
- Lee, Sang Won, et al. "hIL-7-hyFc, a long-acting IL-7, increased absolute lymphocyte count in healthy subjects.” Clinical and Translational Science (2020). [Epub ahead of print] https://doi.org/10.1111/cts.12800
- Choi, Young Woo, et al. "Intravaginal administration of Fc-fused IL7 suppresses the cervicovaginal tumor by recruiting HPV DNA vaccine-induced CD8 T cells." Clinical Cancer Research 22.23 (2016): 5898-5908. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-0423
- Lim, Jun Yeul, et al. "Biophysical stability of hyFc fusion protein with regards to buffers and various excipients." International journal of biological macromolecules 86 (2016): 622-629. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.02.006
- Kang, Moon Cheol, et al. "Intranasal introduction of Fc-fused interleukin-7 provides long-lasting prophylaxis against lethal influenza virus infection." Journal of virology 90.5 (2016): 2273-2284. https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.02768-15
- Seo, Yong Bok, et al. "Crucial roles of interleukin-7 in the development of T follicular helper cells and in the induction of humoral immunity." Journal of virology 88.16 (2014): 8998-9009. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.00534-14
- Ahn, So-Shin, et al. "Nonlytic Fc-fused NT-I7 synergizes with Mtb32 DNA vaccine to enhance antigen-specific T cell responses in a therapeutic model of tuberculosis." Vaccine 31.27 (2013): 2884-2890. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2013.04.029
- Nam, Hyo Jung, et al. "Marked enhancement of antigen‐specific T‐cell responses by IL‐7‐fused nonlytic, but not lytic, Fc as a genetic adjuvant." European journal of immunology 40.2 (2010): 351-358. https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.200939271