SCIENCE
Hyleukin-7TM
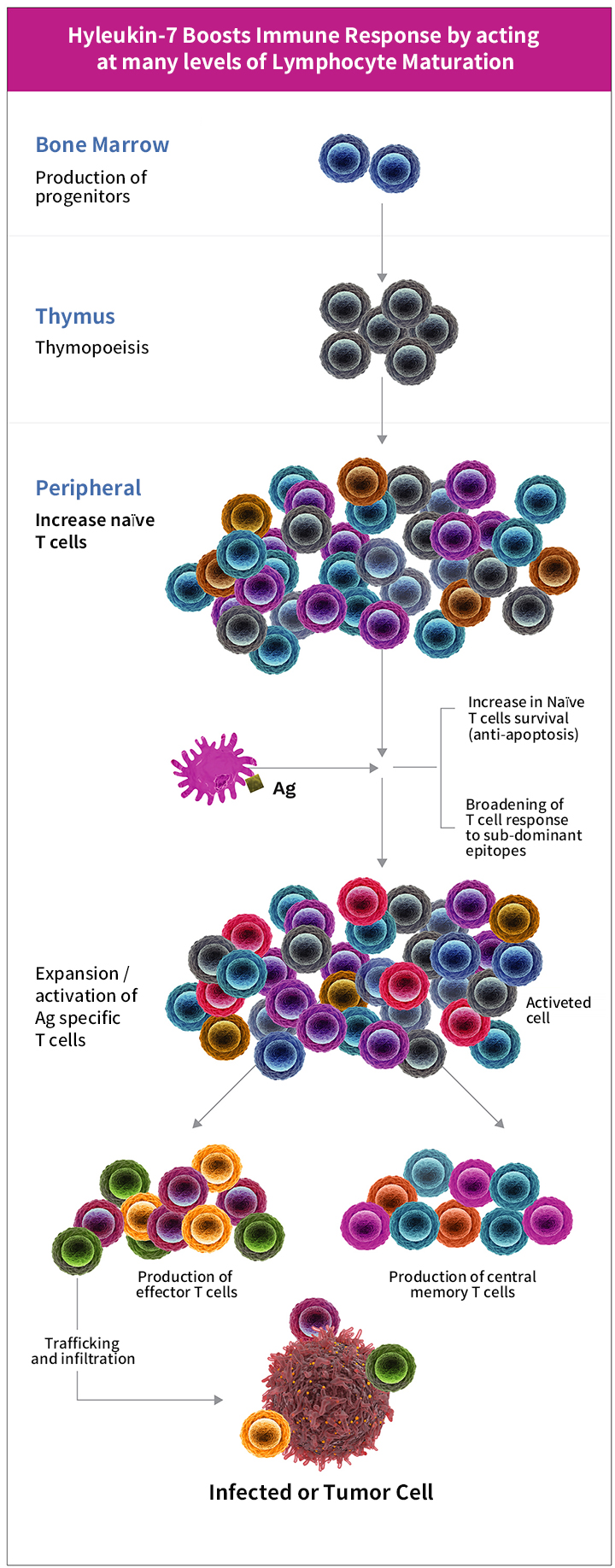
Hyleukin-7TM, a homodimeric IL-7 based growth factor for T cells, is engineered to serve as a stable, long lasting factor for T cell production, maturation, expansion, trafficking, functioning and survival, in multiple levels of T cell production. Hyleukin-7TM is designed with the end-goal of inducing persistent and long-lasting anti-tumor T cell response, as it controls white blood cell production and peripheral homeostasis.
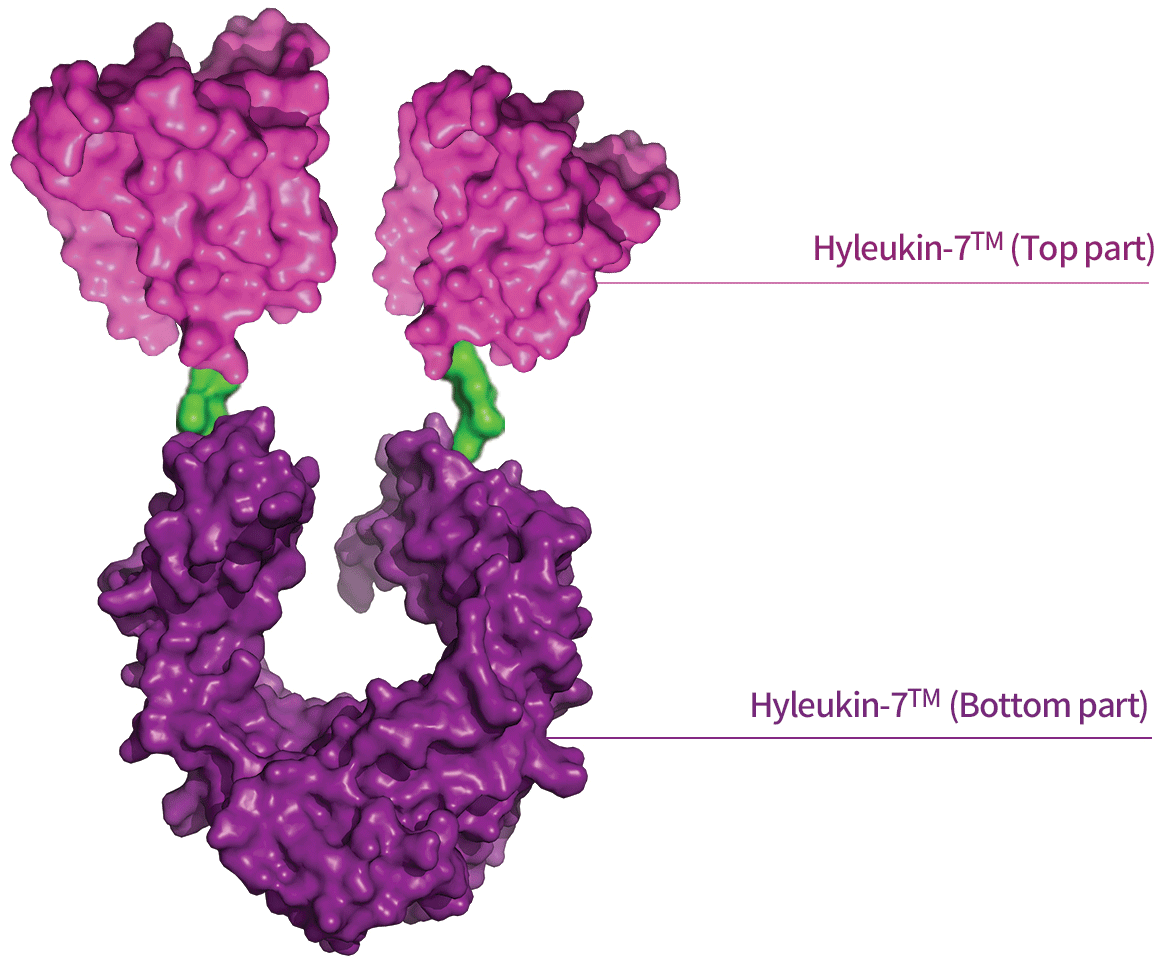
Hyleukin-7TM(Top part): The effector part of Hyleukin-7TM is a stabilized form of Interleukin-7 (IL-7). IL-7, as a therapeutic protein, exhibits poor structural stability and low productivity, that act as intrinsic technical barriers to commercialization. Using advanced protein engineering techniques, we created a stabilized, more effective form of IL-7
Hyleukin-7TM (Bottom part): Hyleukin-7TM is built on the hyFc® platform technology, originating from NIT’s related company, Genexine. hyFc® was used to construct a long-acting fusion protein comprising the engineered IL-7 moiety, hybridized with IgD and IgG4 Fc fragments that serve as a non-cytolytic and non-immunogenic carrier. hyFc® increases the half-life, minimizes the loss of bioactivity of drug candidates, and prevents cell killing effect by ADCC and CDC reactions. For more information about hyFc® technology — http://www.genexine.com/m21.php
Hyleukin-7TM (Bottom part): Hyleukin-7TM is built on the hyFc® platform technology, originating from NIT’s related company, Genexine. hyFc® was used to construct a long-acting fusion protein comprising the engineered IL-7 moiety, hybridized with IgD and IgG4 Fc fragments that serve as a non-cytolytic and non-immunogenic carrier. hyFc® increases the half-life, minimizes the loss of bioactivity of drug candidates, and prevents cell killing effect by ADCC and CDC reactions. For more information about hyFc® technology — http://www.genexine.com/m21.php
Mode of Action in Diseases
Hyleukin-7TM is designed to increase the number of naïve and memory T cells and to enhance T cell functionality. In addition, it is predicted to broaden T cell receptor (TCR) diversity, and consequentially prepare T cells to respond to even subdominant epitopes. Moreover, Hyleukin-7TM will enhance T cell homing and infiltration to tumor by increasing homing chemokine activity and antagonizing various inhibitory networks.
NIT is developing Hyleukin-7TM for diseases with T cell deficiency and malfunction. Our key focusing indications are cancer and lymphopenia. NIT is working in collaboration with major cancer centers and universities in the US and South Korea, pursuing combination trials with leading immunotherapeutics such as immune checkpoint inhibitors, cancer vaccines and more.
The mode of action of Hyleukin-7TM effectively overlaps with cancer immunity cycles, especially at the sites of antigen presentation and tumor microenvironment. Therefore, Hyleukin-7TM could work in a complementary or synergetic means with various cancer treatments targeting a specific immunity cycle or mechanism, such as novel immunotherapeutics.
Lymphopenia is an independent prognostic marker to predict overall survival of cancer patients. Recent publications in the immune-oncology field indicate that cancer patients with lymphopenia exhibit substantially shorter survival time and low response rate to chemo/radiotherapy or immunotherapy.
Cancer
NIT aims at developing Hyleukin-7TM as an enabling drug for cancer therapeutics, by harnessing T cell immunity. Hyleukin-7TM may substantially enhance the efficacy of cancer treatments such as the conventional chemo/radiotherapy, and/or state-of-the-art novel immunotherapies including immune checkpoint inhibitors, cancer vaccines, and more.The mode of action of Hyleukin-7TM effectively overlaps with cancer immunity cycles, especially at the sites of antigen presentation and tumor microenvironment. Therefore, Hyleukin-7TM could work in a complementary or synergetic means with various cancer treatments targeting a specific immunity cycle or mechanism, such as novel immunotherapeutics.
Lymphopenia
Lymphopenia, or lymphocytopenia is the condition of having an abnormally low level of lymphocytes. It causes lowered immune responses to cancer and increased risk of life-threatening infections. Some cancer patients have lymphopenia at the time of diagnosis, and larger portion of patients receiving chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy result in lymphopenia.Lymphopenia is an independent prognostic marker to predict overall survival of cancer patients. Recent publications in the immune-oncology field indicate that cancer patients with lymphopenia exhibit substantially shorter survival time and low response rate to chemo/radiotherapy or immunotherapy.